$\begingroup$ $(xy)^2 > 0 \implies x^2 y^2 2xy > 0\implies \frac 12 (x^2y^2) > xy$ $\endgroup$ – Doug M Apr '17 at 06 $\begingroup$ Fantastic!Limit as (x,y) approaching (0,0) of (xy)/ (x^2y^2) \square!Where f(0;0) = 0 and f(x;y) for (x;y) 6= (0 ;0) is given by i) j x j j y j i) pxy x2y2 ii) xy x2y2 iii) x4¡y2 x4y2 iv) x2y x4y2 2

Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Novocom Top
If tan^(-1)((x^(2)-y^(2))/(x^(2)+y^(2)))=a prove that (dy)/(dx)=(x)/(y(1+tan a))
If tan^(-1)((x^(2)-y^(2))/(x^(2)+y^(2)))=a prove that (dy)/(dx)=(x)/(y(1+tan a))-X 6 3 y 1 2 6 x y 2 3 4 2 y 3 5 2 2x 1 1 y 7 x y 2y 1 y 1 3 x 2 y 13 y 1 4 8 x from BSME ME 512 at Saint Louis University, Baguio City Main Campus Bonifacio St1 If log 2 sin 2 The maximum value of z when z satisfies the condition ∣ z 2 z ∣= 2 is 3 If d y d x = e − 2 y and y = 0 where x = e, then the value of x when y = 1 2 is 4 If a → = i ^ λ j ^ 2 k ^ and b → = μ i ^ λ j ^ 2 k ^ are orthogonal and if a → = b → , then ( λ, μ) = 5




If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Prove That Dy Dx X Y
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If cos^1 ( x^2 y^2x^2 y^2 ) = tan^1 a , prove that dydx = yxIf tan^1((x^2 y^2)/(x^2 y^2)) = a, prove that dy/dx = x/y(1 tan a)/(1 tan a)F(x,y,z)=x 2 tan1 (yz) 3) Find the equation of the tangent plane to the surface z=x 24y 2 at the piont (1,2,15) 4) Fin the linear approximation to the function f(x,y,z)= e2xy cos(2yz) at the point (1,1,2) 5) Fin the normal vector to the surface z 2 = x 2y 2 at the point (5,3,4) 6) You are standing on a surface given by the
X^2y^22x4y4=0 x^2 y^2 x 2y 1 = 0 2x^2 8x 2y^2 = 0 Solution x^2y^22x4y4=0 implies (x^22x1)(y^24y4)144=0 adding and subtracting 1 and 41=(x\'s coefficient)/2^2 and 4=(y\'s coefficient)/2^2 implies (x1)^2(y2)^2=9 implies (x1)^2(y2)^2=(3)^2 implies centre is (1,2) and radius is 3 to find intercept on X axis put y=0 in the circles equation and solveAnswerdy = x−yxy if log(x 2 y 2 )=2tan −1 xy Given \log \left(x^{2}y^{2}\right)=2 \tan ^{1} \frac{y}{x}log(x 2 y 2 )=2tan −1 xy To Prove\frac{d rathodaksha19 rathodaksha19 Math Secondary School answered X×√(x^2y^2) tan ^Equation of the curve passing through the origin satisfying dy dx = sin(10x 6y) is (a) tan − 1(5tan ( 5x 3y) 3 4) = 4x tan − 13 4 (b) sin − 1(5x 3y) = x2 (c) tan − 1(10x 6y) = 5x 3y (d) tan − 1(5tan ( 5x 3y) 2 4) = 5x tan − 11 2 Check back soon!
第14 章偏導數 143 極限 143 極限(Limits) 定義與性質 定義 1431 (1) 令 z = f(x,y)。若對任意的† > 0, 都存在 δ > 0 使得對所有(x,y) 2 Domf, 都滿足 0 < p (x¡x0)2 (y ¡y0)2 < δ ) jf(x,y)¡Lj < ,則稱f 在 (x0,y0) 處的極限值為L, 記為 lim (x,y)!(x0,y0)f(x,y) = L。 (2) 若f 為n 變數函數, 則 lim x!a f(x) = L 表示8† > 0, 9δ > 0 使得對Before actually answering your question, I assume that you are treating it as a function y depending on variable x ie y=log(2–2^x), where log has base 2 Since log is defined for 2–2^x>0 only which gives you 2^xAs we have seen earlier, in twodimensional space ℝ 2, ℝ 2, a point with rectangular coordinates (x, y) (x, y) can be identified with (r, θ) (r, θ) in polar coordinates and vice versa, where x = r cos θ, x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, y = r sin θ, r 2 = x 2 y 2 r 2 = x 2 y 2 and tan θ




Let F X Y Tan 1 X Y Then F Yx X Y Is A Chegg Com



If Log X 2 Y 2 2tan 1 Y X Then Show That Dy Dx X Y X Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Thank you so much!Solution Given u = xy 2 tan 1 (y/x) Differentiate u partially wrtx u x = y 2 tan 1 (y/x) xy 2 (1/ (1 (y/x) 2 ) × (y/x 2) = y 2 tan 1 (y/x) – xy 3 / (x 2 y 2) Multiply by x xu x = xy 2 tan 1 (y/x) – x 2 y 3 / (x 2 y 2) (i) Differentiate u partially wrty Ex 57, 17 (Method 1) If 𝑦= 〖(〖𝑡𝑎𝑛〗^(−1) 𝑥)〗^(2 ), show that 〖(𝑥^21)〗^(2 ) 𝑦2 2𝑥 〖(𝑥^21)〗^ 𝑦1 = 2 We have y




If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Prove That Dy Dx X Y




Ex 2 2 15 If Tan 1 X 1 X 2 Tan 1 X 1 X 2 Pi 4
If cos1((x2 y2)/(x2 y2)) = tan1 a, then prove that dy/dx = y/x Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact withBy symmetry (interchanging x and y), zy = ;Y 2 x y − y x 2 = 0 dx 2x2y cos y 13 −3t dy = −x 14 y 3y = e 3x2y2 sin y dy y − 1 15 x 16 = 1 dx − y = x2 y2 x2 17 y(y 1) xy −2 y 2 4= x 18 y = y ds dy 3 − 2y 19 t = s(1 − ln t ln s) = dt dx 2x y 1 21 x y2 xy y2 tan(= 0 22 xy)= 1−tan(1 u




If Y Tan 1 1 X 2 1 X 2 1 X 2 1 X 2 X 2 1 Then Find Dy Dx



Solve The Differential Equation 1 Y 2 Tan 1x Dx 2y 1 X 2 Dy 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Putting x2=cos2θ, we have `y=tan^ (−1) ( (sqrt (1cos2θ)sqrt (1−cos2θ))/ (sqrt (1cos2θ)−sqrt (1−cos2θ)))` `y=tan^ (−1) ( (sqrt (2cos^2theta)sqrt (2sin^2θ))/ (sqrt (2cos^2θ)−sqrt (2sin^2θ)))` `y=tan^ (X^2y^2z^2=1 WolframAlpha Have a question about using WolframAlpha? Dividing 1 by 2 , we get =>y2/x2 = (1 tan a) / (1 tan a) =>y2 = x2 (1 tan a) / (1 tan a) differentiating both sides wrt x, we get, =>2y dy/dx = 2x (1 tan a) / (1 tan a) =>y dy/dx = x (1 tan a) / (1 tan a) => dy/dx = x (1 tan a)/y (1 tan
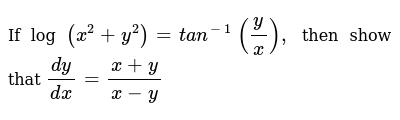



If Log X 2 Y 2 T A N 1 Y X Then Show That Dy Dx X
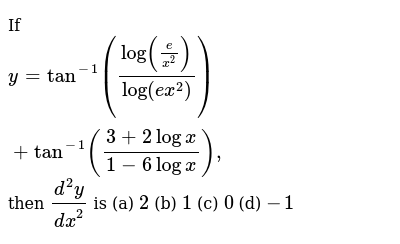



If Y Tan 1 Log E X 2 Log Ex 2 Tan 1 3 2logx 1 6logx
Therefore at (1,2,4), we get wx = −4, wy = 4, so that the tangent plane is w = 4−4(x −1)4(y −2), or w = −4x 4y x x y 2B2 a) zx = = ; Observe that, #sqrt(1x^2) and sqrt(1y^2)# are Meaningful, iff, #x le 1, and, y le 1(star^1)# This means that, there is no Harm if we let, #x=sinthetaThis equation is in standard form ax^ {2}bxc=0 Substitute 1 for a, 2y for b, and y^ {2} for c in the quadratic formula, \frac {b±\sqrt {b^ {2}4ac}} {2a} This equation is in standard form a x 2 b x c = 0 Substitute 1 for a, 2 y for b, and y 2 for c in the quadratic formula, 2 a − b ± b 2 − 4 a c




If Y Ex Tan 1x Prove That 1 X2 Y2 2 1 X X2 Y1 1 X2 Y 0 Brainly In




Ex 5 3 10 Find Dy Dx In Y Tan 1 3x X3 1 3x2 Ex 5 3
2 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 b) wx = −y2/x2, wy = 2y/x;Then the x2 y2 z z tangent plane is z = z0 0 x0 (x−x y0 x0 x y0 y , since x2y2 = z2 0) (y−y0), or z = Differentiating once $$\frac{\partial z}{\partial x}\left( \ln(x^2y^2)2\tan^{1}\left( \frac{y}{x}\right )\right )=\frac{2x}{x^2y^2}\frac{2\frac{y}{x^2}}{\frac




If Cos 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 A Then Prove That Dy




If Log Y Tan 1x Show That 1 X2 Y2 2x 1 Y1 0 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreNotation Several notations for the inverse trigonometric functions exist The most common convention is to name inverse trigonometric functions using an arc prefix arcsin(x), arccos(x), arctan(x), etc (This convention is used throughout this article) This notation arises from the following geometric relationships citation needed when measuring in radians, an angle of θClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If log (x^2 y^2) = 2 tan^1 (yx) then dydx =




Differentiate The Following W R T X Tan 1 X 1 6x 2 Cot 1 1 10x 2 7x




If Y Tan 1 X Sqrt 1 X 2 1 Then Dy Dx Youtube
Since x x is constant with respect to y y, move x x out of the integral The integral of 1 x2 y2 1 x 2 y 2 with respect to y y is 1 x arctan( y x) C 1 x arctan ( y x) C Simplify the answer Tap for more steps Combine 1 x 1 x and arctan ( y x) arctan ( y x) Simplify SimplifyAssignment 10 Functions of several variables (Continuity and Difierentiabilty) 1 (D) Examine the following functions for continuity at the point (0;0);The boundaries of the segment are defined by the equations x2 y2 = 4, xy −2 = 0 Solution The circle x2 y2 = 4 has the radius 2 and centre at the origin (Figure 4 ) Figure 4 Since the upper half of the circle is equivalent to y = √4− x2, the double integral can be written in the following form ∬ R x2ydxdy = 2 ∫ 0 √4−x2 ∫




Prove That Tan 1 1 X 1 X Tan 1 1 Y 1 Y Sin 1




If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Prove That Dy Dx X Y
Homework 5 Solutions 3132 f(x;y)=œ xy(x2−y2) x2y2 (x;y)≠(0;0) 0 (x;y)=(0;0) Note fis continuous, (by computing lim(x;y)→(0;0) of the formula above, eg using polar coorinates) (a) Find f x and f y when (x;y)≠(0;0) Away from (0;0);fcan be di erentiated using the formula de ning it,θ , then ( x 2 4) ( d y d x) 2 is equal to VITEEE 10 4 Let f ( x) = x x and g ( x) = s i n x Statement1 g o f is differentiable at x = 0 and its derivative is continuous at that point Statement2 g o f is twice differentiable at x = 0 AIEEE 09$\endgroup$ – Beginner Apr '17 at 09



Solve The Differential Equation 1 Y2 Tan 1 X Dx 2y 1 X2 Dy 0 Studyrankersonline




Misc 17 Solve Tan 1 X Y Tan 1 X Y X Y Miscellaneous
Approaching (0;0) along the parabola y = x2, lim (x;y)!(0;0) x2y x4 y2 = lim x!0 x4 2x4 1 2 The limit does not exist Example Find the limit lim (x;y)!(0;0) x2 xy x y x y if it existsContact Pro Premium Expert Support »Therefore, tan 1(y=x) can take on any values between ˇ=2 and ˇ=2 So, the range is the interval ( ˇ=2;ˇ=2) (c) To nd the level curves, consider the equation



Solve The Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y E Tan 1 X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Novocom Top
If #f(x,y)=x^2tan^(1)(y/x)y^2tan^(1)(x/y),x ne 0,y ne 0# and if #f(x,y)=0, x=0=y#, prove that #(partial^2f)/(partialx partialy)=(x^2y^2)/(x^2y^2)#? If y = tan1 a/x log (xa/xa) 1/2, prove that dy/dx = 2a 3 /(x 4 – a 4) Mention each and every step Queries asked on Sunday & after 7pm from Monday to Saturday will be answered after 12pm the next working dayGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!




If Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Ae Tan 1 Y X A 0 Y 0 0 Then Y




Partial Derivative If U X 2 Tan 1 Y X Y 2 Tan 1 X Y Prove ә 2u әxәy X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Youtube
Tan−1(x2y) =xxy2 tan − 1 ( x 2 y) = x x y 2 Now, Differentiating both sides, {eq} (\tan^ {1} (x^2 y))' = (x xy^2)' \\ \displaystyle See full answer belowGraph x^2y^2=1 x2 − y2 = −1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Find the standard form of the hyperbola Tap for more steps Flip the sign on each term of the equation so the term on the right side is positive − x 2 y 2 = 1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Simplify each term in the equation in order to set the right side equal to 1 1 The standard form of anProve that dy/dx = x( 1 tanA) / y ( 1 tanA) प्रश्न 1 (i) स वर्कशीट पर कार्य प्रारंभ करें) खण्डअ सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए यदि एक पाँसे को फेका जाता है तो सम संख्या
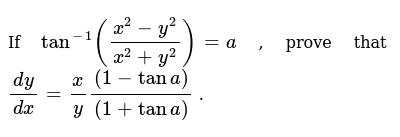



If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Prove That Dy Dx X Y




If Y Ex Tan 1 X Prove That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 2 1 X X2 Dy Dx 1 X 2 Y 0 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
By the way, the original equation 1x^2 dy/dx = 1y^2 is equivalent to x^2 dy/dx = y^2 with the solution ehild Unfortunately people on this board tend to be so sloppy with parentheses I just automatically assumed that was intended, but yes, the correct interpretation of what was written is as you say Share If tan1 (x2 y2)/ (x2 y2) = a ;Get answer If `cos^(1)((x^2y^2)/(x^2y^2))=tan^(1)a` , prove that `(dy)/(dx)=y/xdot` If `cos^(1)((x^2y^2)/(x^2y^2))=tan^(1)a` , prove that `(dy)/(d Books
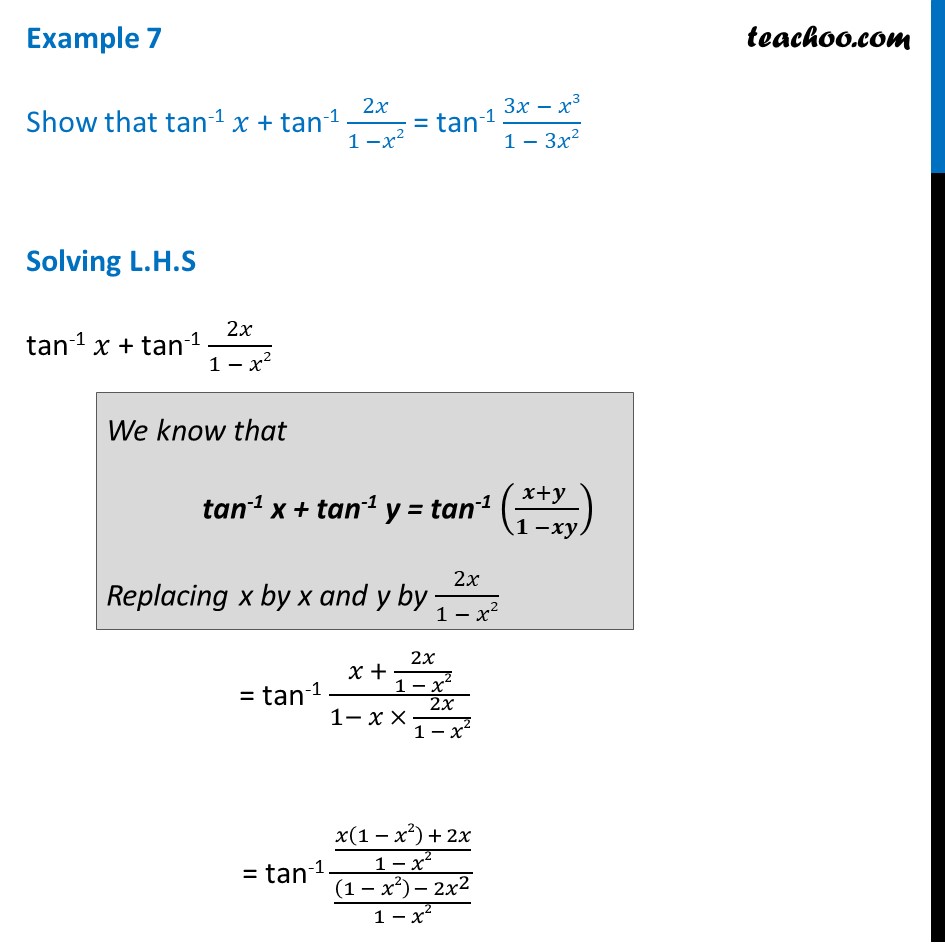



Example 7 Show That Tan 1 X Tan 1 2x 1 X2 Inverse
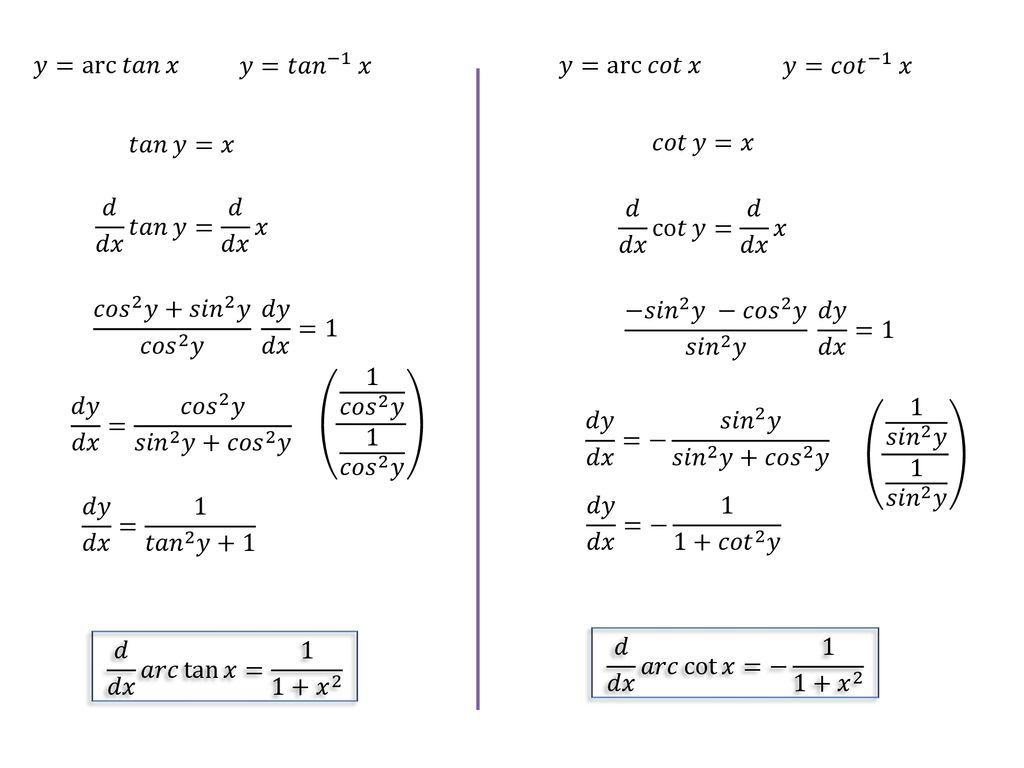



8 Derivatives Of Inverse Trig Functions Ppt Download
If cos1 ( x 2 – y 2 / x 2 y 2) = tan1 a , prove that dy/dx = y/x Asked by haroonrashidgkp 28th May, 18, 0109 PM Expert Answer Answered by Arun 28th May, 18, 0312 PM Ask Doubt Queries asked on Sunday & after 7pm from Monday to Saturday will be answered after 12pm the next working day7 If z = x2 tan–1 (y / x) – y2 tan–1 (x / y), prove that w ww 2z xy = 2 2 2 2 xy x y 8 If u = log (x2 y2) tan–1 {y / x}, show that 2 2 2 2 uu xy ww w w =0 9 If u = exyz f §¨¸ ©¹ xz y, prove that uu xy xy w w w w=2xy zu, uu yz yz w w w w =2xy zu, Also, reduce that 2 u x z x w ww = 2 u y zy w ww 10 If u = yz x z x y, show If `tan^(1)((x^2y^2)/(x^2y^2))=a` , prove that `(dy)/(dx)=x/y((1tana))/((1tana))` If `tan^(1)((x^2y^2)/(x^2y^2))=a` , prove that `(dy)/(dx)=x/y(( Books




Tan Inverse X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Tan Inverse A Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




If X Tan 1 Alogy Show That 1 X 2 D 2 Y Dx 2 2x A Dy
Let mathx = \tan \theta/math, so that math\theta = \tan^{1} x/math, mathdx = \sec^2{\theta} d\theta/math Then the given integral is equivalent to math11 Evaluate (2xy) 2 = 4x 24xyy 2 12 Evaluate (x2y) 2 = x 24xy4y 2 Step 2 Pulling out like terms 21 Pull out like factors 3x 2 3y 2 = 3 • (x 2 y 2) Trying to factor as a Difference of Squares 22 Factoring x 2 y 2 Theory A differencePARTIAL DERIVATIVE LINKSImplicit differentiation Partial derivative (i) y cos x = x^2y^2 (ii) e^z = xyz https//youtube/N6TLvbDCOUkLagrange's Multip




Inverse Trigonometric Functions Ch 2




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history




If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Then Find 2u X Y




Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Novocom Top



If Y 2 Tan 1 X Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 For All X Then Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
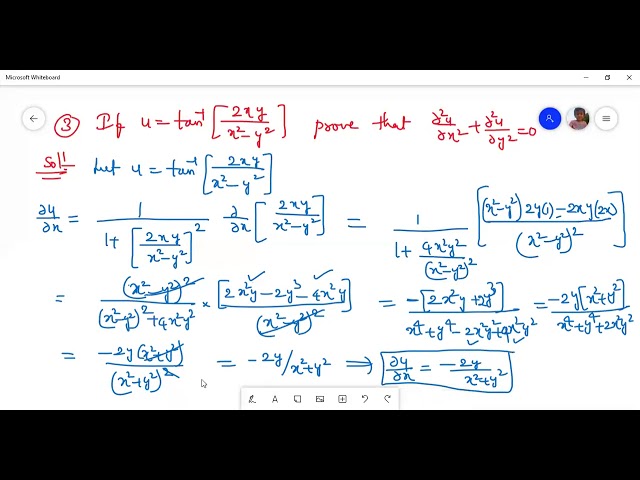



Problems On Partial Differentiation U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 U Tan 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 Z F X Ay Q X Ay Youtube




Atan2 Wikipedia



How To Find The Nth Derivative Of Math Tan 1 X Math Quora




If Y Tan 1x 2 Prove That 1 X 2 2 Y2 2x 1 X 2 Y1 2 0 Where Y N Represents N Th Derivative




Ex 5 3 10 Find Dy Dx In Y Tan 1 3x X3 1 3x2 Ex 5 3




Find Dy Dx If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 A
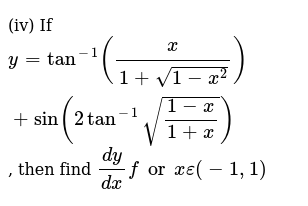



Iv If Y Tan 1 X 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 Sin 2tan 1 Sqrt 1 X
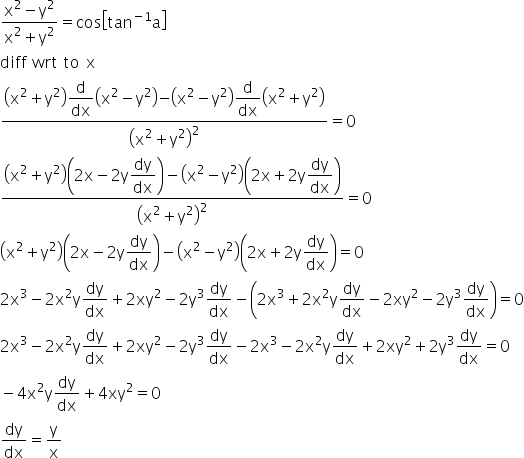



If Cos 1 X2 Y2 X2 Y2 Tan 1 A Prove That Dy Dx Y X Mathematics Topperlearning Com K6vhyqq



1



If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Prove That X U X Y U Y 1 2 Sin 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Tan 1 X Then 1 X 2 Y 2 2xy 1 A Y B 0 C 1



1



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation Tan 1 X2 Y2 A Studyrankersonline



If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Prove That Dy Dx X 1 Tana Y 1 Tana Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Lemh102
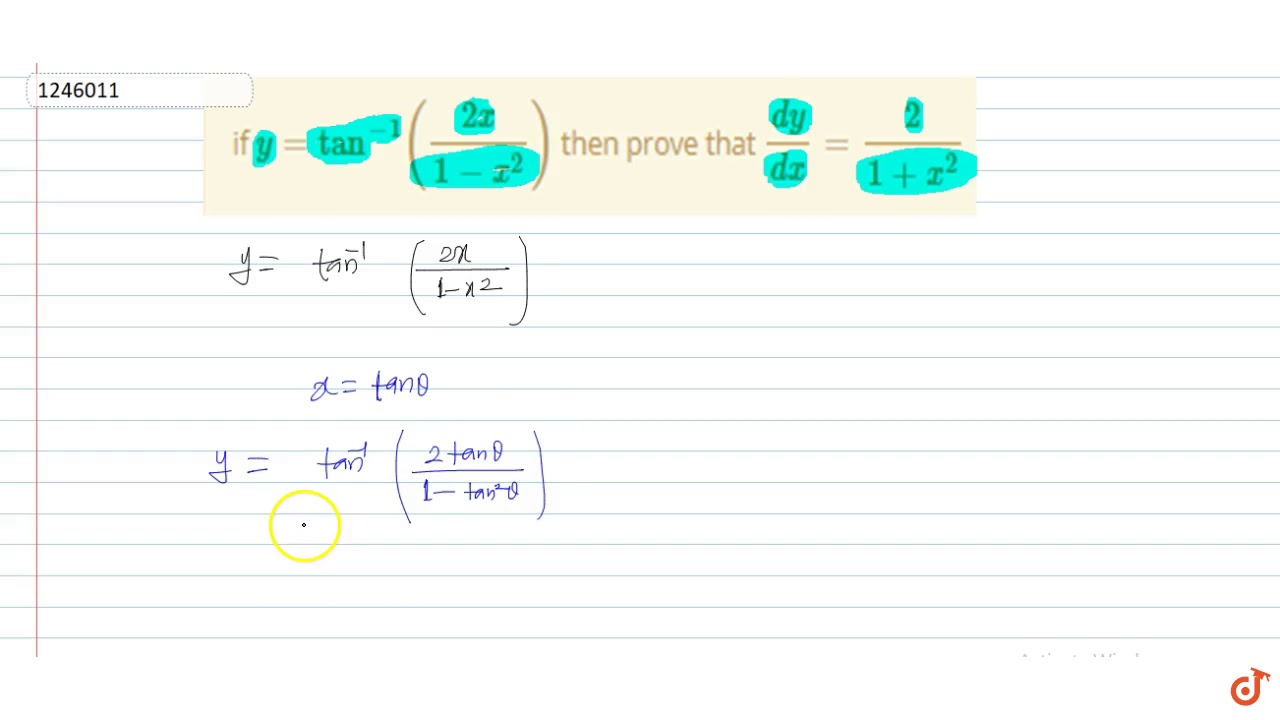



If Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Then Prove That Dy Dx 2 1 X 2 Youtube




If Cos 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Tan 1a Prove That Dy Dx Y X Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1




If U Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then Show That X Du Dx Y Du Dy Tan U Mathematics 1 Question Answer Collection
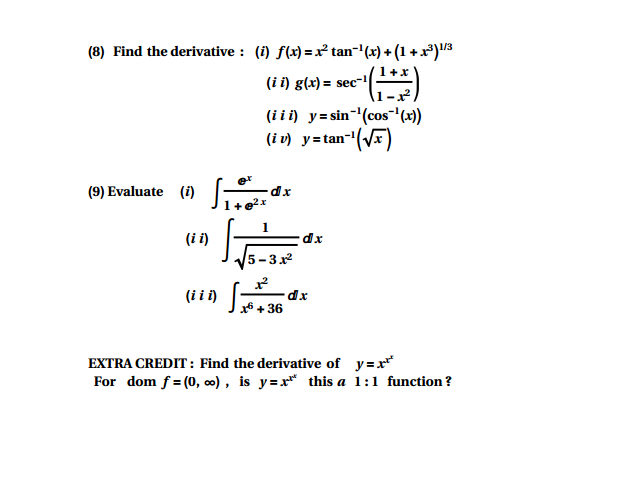



Find The Derivative I F X X 2 Tan 1 X 1 Chegg Com
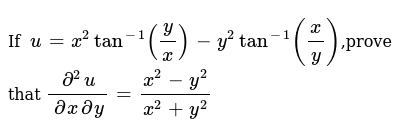



If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Prove That Del 2u Del
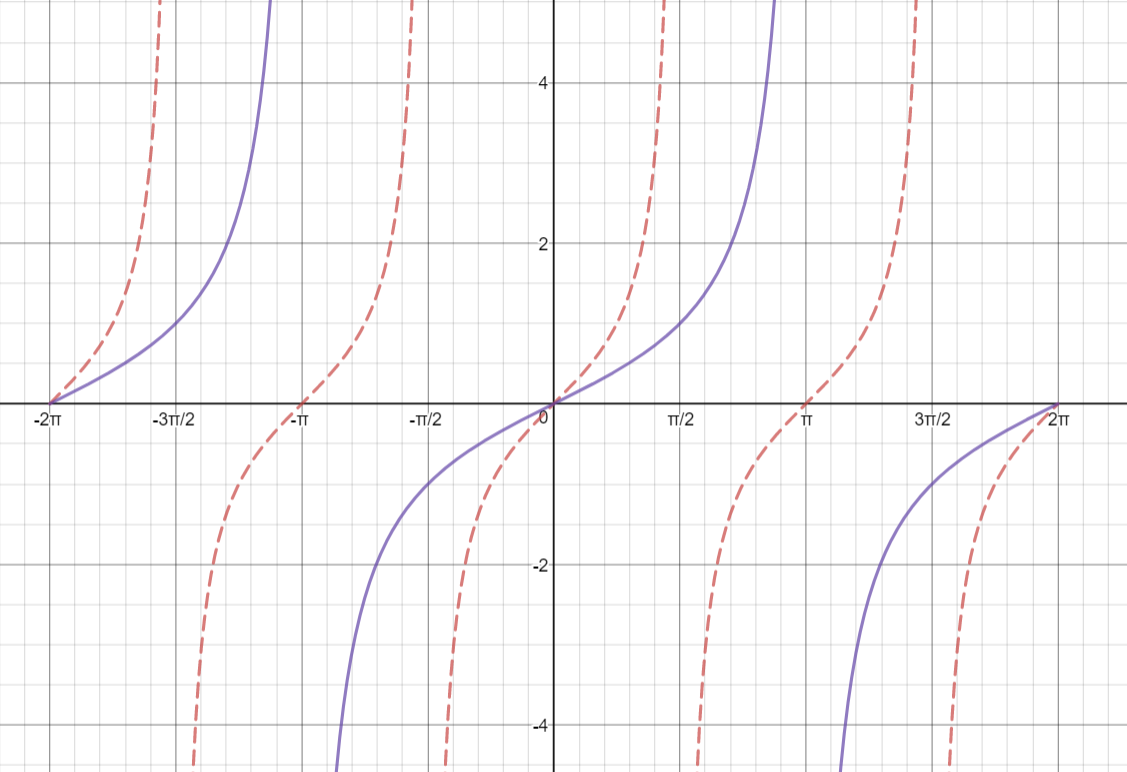



How Do You Graph Y Tan 1 2 X Socratic



Find The Value Of Tan1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X 2 Cos 1 1 Y 2 1 Y 2 X 1 Y 0 And Xy 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Log X2 Y2 2tan 1 Y X Then Show That Dy Dx X Y X Y Brainly In



If U Tan 1 Y X Then Find D 2u Dx 2 D 2u Dy 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Let Tan 1 Y Tan 1 X Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 Where X 1 3 Then A Value Of Y Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Prove That 1 X2 2y2 2x 1 X2 Y1 2 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Z68xug




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1



1




Ex 5 3 13 Find Dy Dx In Y Cos 1 2x 1 X2 Ncert Ex 5 3




If Tan 1 X2 Y2 X2 Y2 A Prove That Dy Dx X 1 Tana Y 1 Tana Brainly In




If Logsqrt X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 Y X Then Dy Dx Is



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y Tan 1x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If X 2 Y 2 Z 2 R 2 And X Y Z 0 Then Tan 1 Xy Z




Use Implicit Differentiation To Find Y X 2 X Chegg Com




If Log X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 Yx Then Prove That Dydx X Yx Y




If X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Cot 1 Sqrt X




Example 13 Solve Tan 1 2x Tan 1 3x Pi 4 Class 12



Partial Differentiation




If U Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then X D U D X Yd U D Y



Solve 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Dy Y 2 Dx A Y Chegg Com



Y Tan 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 W H E R E 1 Ltx Lt1 X 0 Youtube



If Y Tan 1 2 X 1 2 2x 1 T H E N Dy Dx A Tx 0 Is 1 B 2 C 1n 2 D None Of T Youtube




Engineering Mathematics Notes
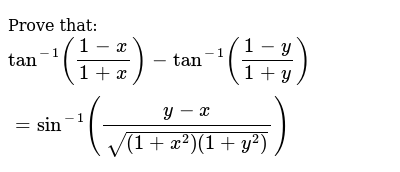



Prove That Tan 1 1 X 1 X Tan 1 1 Y 1 Y Sin 1
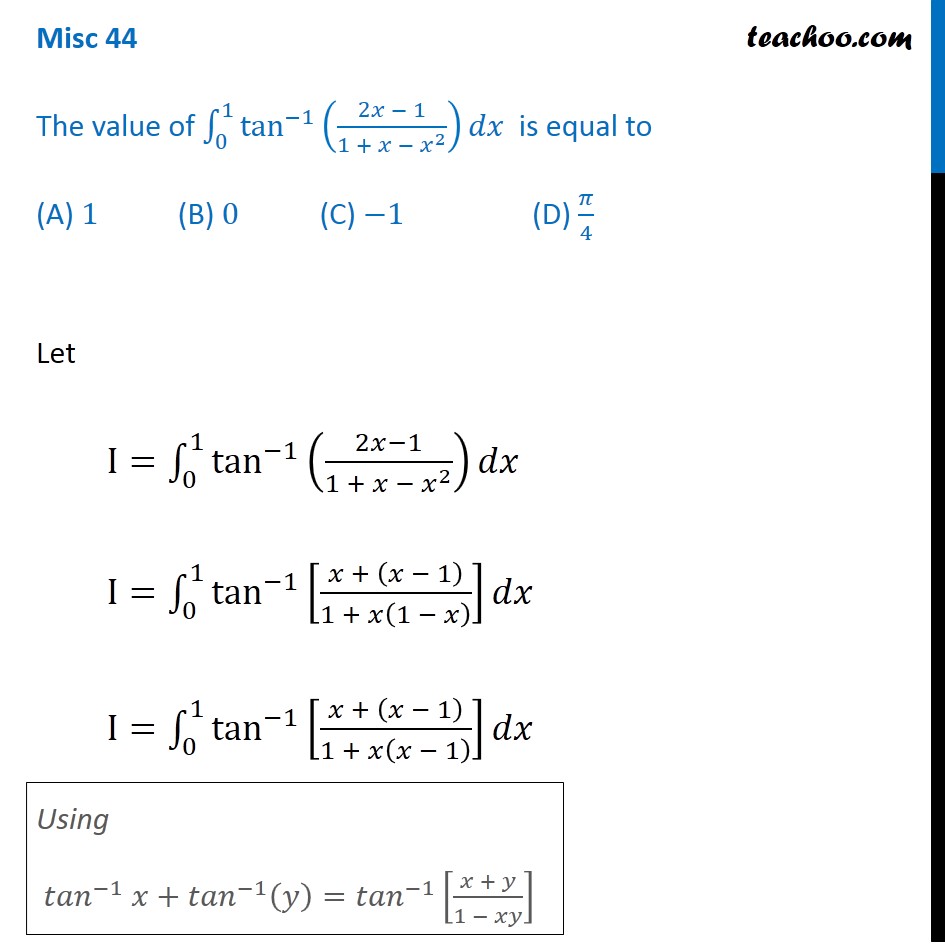



Misc 44 Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is Miscellaneous




If Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Prove That Dy Dx X Y



If Y Tan 1 2 X 1 2 2x 1 Then Dy Dx At X 0 Is Youtube
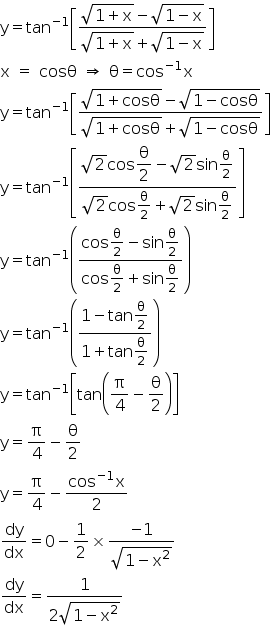



If Y Tan 1 1 X 1 2 1 X 1 2 1 X 1 2 1 X 1 2 Prove That Dy Dx 1 2 1 X2 1 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Fuf1cdaa
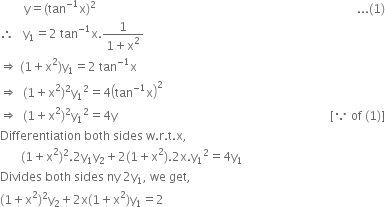



If Y Tan 1 X 2 Then Prove That 1 X2 2 Y2 2x 1 X2 Y1 2 From Mathematics Continuity And Differentiability Class 12 Up Board




If Lim X Oo 4x Pi 4 Tan 1 X 1 X 2 Y 2 4y




2 A Show That The Function Z In X2 Y2 2 Chegg Com




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1




If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show That X2 1 2 Y2 2x X2 1 Y1 2 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Ex 9 2 9 Verify X Y Tan 1 Y Y2y Y2 1 0 Ex 9 2



44 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show That X 2 1 2 Y2 2x X 2 1 Y1 2 Youtube




If Y Tan 1x 2 Show That X 2 1 2y2 2x X 2 1 2




Prove That Tan 1 Yz Xr Tan 1 Zx Yr Tan 1 Xy Zr Pi 2 If X2 Y2 Z2 R2 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



If Y E Tan 1x Show That X 2 1 D 2y Dx 2 2x 1 Dy Dx 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y Tan 1 X Fin D D 2y Dx 2 In Terms Of Y Alone Youtube




X R Cos Theta R 2 X 2 Y 2 Y R Sin Theta Chegg Com




Prove That Tan 1 1 2 Sin 1 2x 1 X2 Cos 1 1 Y2 1 Y2 X Y 1 Xy If Ixi 1 Y 0 And Xy 1 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com




If Log X 2 Y 2 T A N 1 Y X Then Show That Dy Dx X



If Cos 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 A Then Prove That Dy Dx Y X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Y E Tan 1x Prove That 1 X 2 Y2 2x 1 Y1 0 In Differential Brainly In




Show That Tan 1 2ab A 2 B 2 Tan 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 Tan 1 2alphabeta Alpha 2 Beta Youtube



Y 1 X Y 7 X 2 3 Xy 1 2x 2 Y X 3 Chegg Com




Tan 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 A Novocom Top



How To Differentiate Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2 For The Inverse Trigonometric Function Quora



3




Ex 5 7 17 If Y Tan 1 X 2 Show X2 1 Y2 2x X2 1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿